

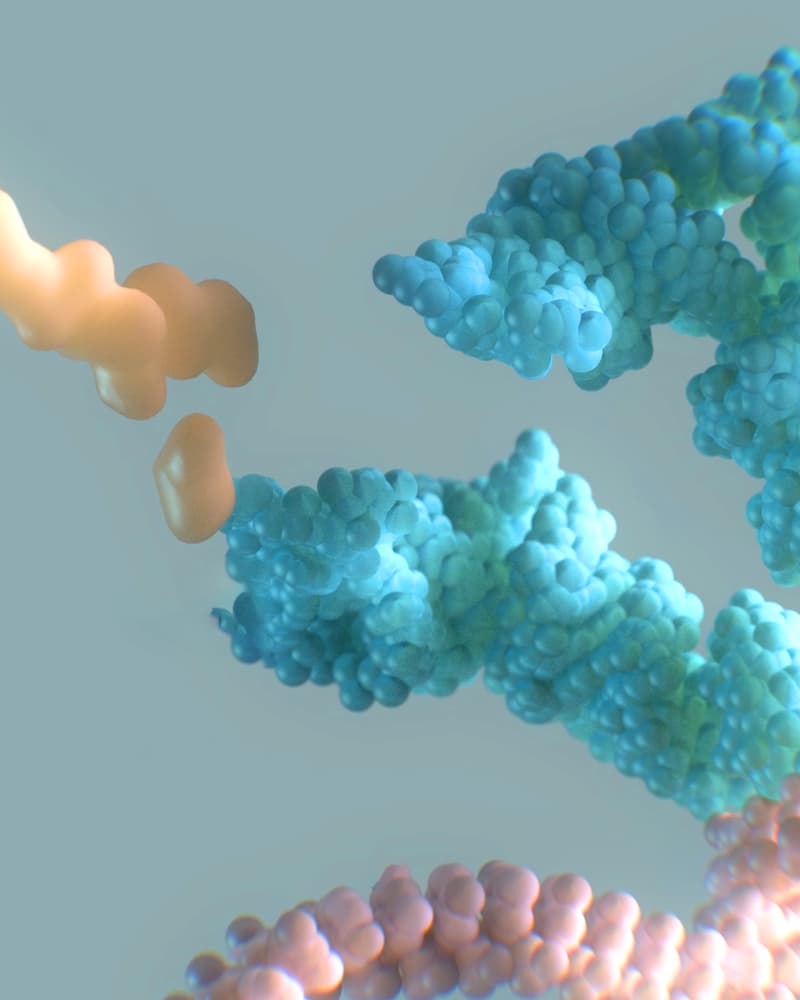
latent catalytic site
: a dormant surface region of a protein that can catalyze bond formation when engaged by a molecule with the right electronic signature
 Flashcards Listing
Flashcards Listing


: a dormant surface region of a protein that can catalyze bond formation when engaged by a molecule with the right electronic signature


: farm management practices that restore soil health, encourage biodiversity, safeguard water resources, and increase climate resilience while reducing greenhouse gas emissions and increasing productivity and profitability


: an artificial intelligence (AI) training technique based on trial and error that uses positive and negative feedback to teach the AI to perform a desired task in accordance with maximizing positive feedback


: a biologic synthesized entirely from nontraditional amino acids


: a permit representing one metric tonne of carbon dioxide that is generated by quantifying and verifying the impact of nature-based methods in either avoiding carbon emissions or increasing the amount of carbon stored in the land


: biotechnologies that enable intentional and repeatable generation of medicines across many diseases or products for agriculture and sustainability

: an RNA molecule that decodes mRNA and transfers the appropriate amino acid to the growing polypeptide chain


: the accumulated hours of cool winter temperatures that certain fruit and nut trees need during dormancy to prepare for flowering and fruiting in the spring and summer


: greenhouse gas emissions from sources not owned or controlled by an organization, occurring upstream or downstream in its supply chain


: therapeutic modalities based on biological building blocks that can be rationally designed and arranged to achieve a desired effect


: the trillions of microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, archaea, protozoa, and fungi, that are found within and on the human body


: the capacity of soil to function as a living ecosystem that sustains plants, animals, and people


: a dormant surface region of a protein that can catalyze bond formation when engaged by a molecule with the right electronic signature
Proteins once considered “undruggable” — too smooth or featureless for traditional small molecule medicines to bind — may hold untapped potential. On their surfaces, are latent catalytic sites, pockets that can form new chemical bonds with certain molecules. By identifying molecules with the right electronic fingerprint, scientists can design drugs that reach targets once thought inaccessible.
Learn how Flagship-Founded Expedition Medicines is combining artificial intelligence, quantum chemistry, and covalent drug discovery to unlock latent catalytic sites.


: farm management practices that restore soil health, encourage biodiversity, safeguard water resources, and increase climate resilience while reducing greenhouse gas emissions and increasing productivity and profitability.
Soil health is a primary concern for farmers who adopt regenerative practices as healthy soils resist erosion, maximize water infiltration, and improve nutrient cycling. This increases profitability by producing higher yield with fewer inputs.


: an artificial intelligence (AI) training technique based on trial and error that uses positive and negative feedback to teach the AI to perform a desired task in accordance with maximizing positive feedback
This machine learning paradigm has been used to famously train AI to beat the world’s foremost Go and chess champions but it can also be applied to teach machines to pursue other goals, such as optimizing biomolecular designs.


: a biologic synthesized entirely from nontraditional amino acids
Digitally designed and chemically synthesized, these protein medicines are engineered to exhibit supranatural properties that surpass the therapeutic reach of traditional biologics. Synteins™ medicines offer the possibility of less frequent dosing and oral delivery, access to parts of the human body that were previously impossible to treat, and longer lasting effects than conventional biologics.
Learn how Flagship-founded Abiologics is leveraging artificial intelligence and chemistry to create Synteins™.


: a permit representing one metric tonne of carbon dioxide that is generated by quantifying and verifying the impact of nature-based methods in either avoiding carbon emissions or increasing the amount of carbon stored in the land.
Growers who adopt farming practices that reduce or avoid emissions can produce carbon credits for the voluntary market once the impact of these practices are quantified and verified. Companies or individuals can purchase credits to mitigate the impact of emissions from their operations that cannot be reduced, removed, or avoided.
Learn more about Flagship-founded Indigo Ag's carbon credit program.


: biotechnologies that enable intentional and repeatable generation of medicines across many diseases or products for agriculture and sustainability
The power and value of a bioplatform relates to the degree with which it serves a diversity and breadth of applications and can be universally applied.


: an RNA molecule that decodes mRNA and transfers the appropriate amino acid to the growing polypeptide chain
Beyond properly positioning amino acids in the final protein product, tRNA is involved in an entire biological framework for coordinating multicellular life.
Learn how Flagship-founded Alltrna is pioneering tRNA therapeutics to treat thousands of diseases that share the same genetic mutation.


: the accumulated hours of cool winter temperatures that certain fruit and nut trees need during dormancy to prepare for flowering and fruiting in the spring and summer
After the first frost, trees like peaches, pears, and cherries enter a rest period that is essential for their productivity. Each variety requires a specific number of chill hours to flower properly. But as winters warm, this natural reset is increasingly disrupted — leading to weaker blooms and reduced yields.
Learn how Flagship-founded Terrana Biosciences is pioneering RNA-based agricultural solutions to deliver protective and enhanced crop traits designed to help crops thrive despite variable climate conditions like warmer winters.


: greenhouse gas emissions from sources not owned or controlled by an organization, occurring upstream or downstream in its supply chain.
While organizations do not have direct control over these emissions sources, they can influence reduction by selecting suppliers with a low carbon footprint or lengthening the useful lifespan of a product.
Learn more about Flagship-founded Indigo Ag and CIBO Technologies' programs and solutions for scope 3 emissions


: therapeutic modalities based on biological building blocks that can be rationally designed and arranged to achieve a desired effect
The fusion of computation and biology is enabling the development of new medicines with predictable outcomes.


: the trillions of microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, archaea, protozoa, and fungi, that are found within and on the human body
These microbes play important roles in human health. Interventions can target imbalances in these communities to restore homeostasis and affect the progression of a wide variety of diseases.
Learn how Flagship-founded Seres Therapeutics is pioneering microbiome therapeutics.


: the capacity of soil to function as a living ecosystem that sustains plants, animals, and people
Healthy soil supports more than just yield — it retains water during drought, drains during floods, recycles nutrients, and anchors beneficial microbes that help plants thrive. Improving soil health through regenerative farming practices like cover cropping and reduced tillage can lower input costs, increase resilience to climate extremes, and even unlock new revenue through carbon credits.


: nature-based sustainability initiatives upstream or downstream of a company’s operations that reduce greenhouse gas emissions and increase carbon storage, enhancing the carbon emissions reduction capacity of a supply chain.
While offsets compensate for excessive emissions by funding external sustainability projects, insets proactively look for opportunities to reduce emissions within a company’s sphere of influence. The focus is on embedding practices with a positive environmental impact in the supply chain rather than removing practices with negative impacts.


: a type of mathematical system, inspired by the network of neurons of the human brain, that finds statistical patterns in very large datasets to predict and generate the most probable content following an initial prompt
Models can be trained using biological datasets to infer the complex and highly dynamic “language of biology.” For example, from a protein sequence, a model could predict protein structures, or from a genetic sequence, predict a relevant promoter region.


: the use of vast computational power to create biological designs with desired properties by inferring the principals of biology from large datasets
The future of drug development will be defined by the ability to generate, rather than discover, drugs with desired therapeutic effects, optimized costs, and reduced or eliminated off-target effects.


: a new class of therapeutics that reprogram diseased cells to release a defined array of signals that precisely coordinate multicellular networks to drive disease resolution
Diseased cells can send pathologic signals to other cell types in their network, perpetuating a cycle of dysfunction and disease progression. Yet drug development has traditionally focused on affecting only one cell type in the network. Network Medicines are designed to have both a direct effect by targeting the diseased cells themselves and a network effect by reprogramming diseased cells to release therapeutic signals that coordinate other key cells in the network to restore health.
Learn how Flagship-founded Sonata Therapeutics is designing Network Medicines™ that reprogram diseased cells to become the coordinators of cure.


: protecting, maintaining, or improving people's health before they get sick by providing interventions targeted to pre-disease states for those that are seemingly healthy but at risk
Interventions protect health from external threats (i.e., health security) and prevent or delay the onset of diseases (i.e., preemptive medicine).
Learn more about Flagship's Preemptive Health & Medicine Initiative.


: the study of genetic variation found within each cell of a multicellular organism
All cells accumulate random genetic changes in their DNA. As a result, an individual’s genome is not a single genome but trillions of unique genomes throughout the body. While variations may have no apparent impact, some impart disease resistance and others cause or increase vulnerability to disease. It is as if clinical trials for these mutations are being conducted at the cellular level. Tapping into this trove of information opens up new opportunities to cure, prevent, or reverse disease.
Learn how Flagship-founded Quotient Therapeutics is pioneering somatic genomics.


: the synthesis of machine, human, and nature’s intelligence to form a collaborative network that leverages the creativity and imagination of humans, the adaptive problem-solving capabilities of nature, and the speed and scale of machines
This reimagining of intelligence is sparking a modern technological renaissance, enabling us to think, create, and innovate at a depth and scale that can produce solutions to some of the world’s most intractable, contemporary challenges.
Learn more on how Flagship is leveraging polyintelligence to revolutionize biotechnology.


: the use of genetic code to discover the foundations of small molecule medicines
Enzymatic proteins encoded in genes make and modify bioactive small molecules. From human samples, we can pinpoint the biosynthetic gene clusters that give rise to these molecules, revealing the instructions for small molecule drug leads that can be matched to disease-relevant targets.
Learn how Flagship-founded Empress Therapeutics is leveraging genetic chemistry to source chemistry from within the human body.


: any genetically driven disease that stems from a premature termination codon mutation, which prevent the formation of a complete and functional protein
Reclassifying patients based on their shared mutation, rather than individual mutated gene or traditionally defined clinical presentation, could unify treatment for seemingly disparate diseases.
Learn how Flagship-founded Alltrna is pioneering tRNA therapeutics to treat thousands of diseases.


: farming practices that leverage nature-based methods to increase atmospheric carbon sequestration in plant biomass and soil and decrease greenhouse gas emissions.
Plants convert carbon in the atmosphere to a form they can use via photosynthesis. When the plant biomass decomposes, microbes convert that material into soil organic carbon. Farmers can work with nature to prevent carbon from leaching into the atmosphere and increase the amount that is stored in their land.
Learn more about Flagship-founded Indigo Ag's carbon farming program.


: the process of changing which type of hemoglobin a red blood cell produces, shifting from adult sickled hemoglobin to fetal hemoglobin as a therapeutic approach to sickle cell disease
In people with sickle cell disease, increasing fetal hemoglobin (HbF) prevents red blood cells from sickling and blocking blood vessels. Reactivating HbF is a recognized therapeutic strategy that can significantly lessen disease burden.
Learn how Cellarity is advancing globin switching as a therapeutic approach to sickle cell disease.


: a level of intelligence that surpasses the existing intellect of both humans and nature and leverages the full spectrum of human scientific knowledge and the adaptive intelligence derived from nature's evolutionary processes
By integrating machine intelligence into every step in the scientific method, we enable AI to move beyond the limits of known information. This allows the creation of scientific knowledge at a scale, speed, and precision that far surpasses current human capabilities, driving solutions to humankind’s greatest challenges.
To learn how Flagship is on a mission to achieve scientific superintelligence, visit Lila.


: the computational challenge of determining the amino acid sequence that produces a desired protein structure
The structure of a protein impacts how it functions and behaves in an environment, particularly how it binds with other molecules. If scientists could determine the amino acid sequence that would provide a desired structure, it would take much of the guesswork out of developing biologic medicines.


: growing practices that protect, maintain, and enhance ecosystems.
Instead of depleting natural resources, food production can be a vehicle for delivering positive outcomes for nature, people, and the climate.


: a genome engineering technology based on mobile genetic elements that consists of a protein and an RNA or DNA template to effect a therapeutic change
By only nicking the DNA, rather than making a double-stranded break, Gene Writers can substitute a single base pair; delete or insert short DNA sequences; or write in entire genes into the human genome.
Learn how Flagship-founded Tessera Therapeutics’ Gene Writing™ technology has the potential to treat diseases at their source.


: environmental factors that negatively impact plant health
Biotic stresses come from living threats like pests, fungi, and bacteria. Abiotic stresses stem from non-living factors such as drought and floods, temperature extremes, and air pollution. These threats can limit growth, reduce yields, and threaten food security. Advances in crop genetics, biological treatments, and regenerative practices can help farmers enhance crop resilience under variable and extreme conditions.


: products used to combat stressors and promote crop health, derived from or inspired by naturally occurring substances and organisms.
Farmers use biological crop protection to help crops perform under pressure while reducing reliance on synthetic chemicals and their environmental impact. These tools can enhance disease resistance, improve water and nutrient use efficiency, and increase resilience to heat, drought, and pests — supporting both yield and long-term soil health.